Relation mode
In Prisma, relations between records are defined with the @relation attribute. For example, in the following schema there is a one-to-many relation between the User and Post models:
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id], onDelete: Cascade, onUpdate: Cascade)
authorId Int
}
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
posts Post[]
}
Prisma has two relation modes, foreignKeys and prisma, that specify how relations between records are enforced.
If you use Prisma with a relational database, then by default Prisma uses the foreignKeys relation mode, which enforces relations between records at the database level with foreign keys. A foreign key is a column or group of columns in one table that take values based on the primary key in another table. Foreign keys allow you to:
- set constraints that prevent you from making changes that break references
- set referential actions that define how changes to records are handled
Together these constraints and referential actions guarantee the referential integrity of the data.
For the example schema above, Prisma Migrate will generate the following SQL by default if you use the PostgreSQL connector:
-- CreateTable
CREATE TABLE "Post" (
"id" SERIAL NOT NULL,
"title" TEXT NOT NULL,
"authorId" INTEGER NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT "Post_pkey" PRIMARY KEY ("id")
);
-- CreateTable
CREATE TABLE "User" (
"id" SERIAL NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT "User_pkey" PRIMARY KEY ("id")
);
-- AddForeignKey
ALTER TABLE "Post"
ADD CONSTRAINT "Post_authorId_fkey"
FOREIGN KEY ("authorId")
REFERENCES "User"("id") ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;
In this case, the foreign key constraint on the authorId column of the Post table references the id column of the User table, and guarantees that a post must have an author that exists. If you update or delete a user then the ON DELETE and ON UPDATE referential actions specify the CASCADE option, which will also delete or update all posts belonging to the user.
Some databases, such as MongoDB or PlanetScale, do not support foreign keys. Additionally, in some cases developers may prefer not to use foreign keys in their relational database that usually does support foreign keys. For these situations, Prisma offers the prisma relation mode, which emulates some properties of relations in relational databases. When you use Prisma Client with the prisma relation mode enabled, the behavior of queries is identical or similar, but referential actions and some constraints are handled by the Prisma engine rather than in the database.
There are performance implications to emulation of referential integrity and referential actions in Prisma Client. In cases where the underlying database supports foreign keys, it is usually the preferred choice.
How to set the relation mode in your Prisma schema
To set the relation mode, add the relationMode field in the datasource block:
datasource db {
provider = "mysql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
relationMode = "prisma"
}
The ability to set the relation mode was introduced as part of the referentialIntegrity preview feature in Prisma version 3.1.1, and is generally available in Prisma versions 4.8.0 and later.
The relationMode field was renamed in Prisma version 4.5.0, and was previously named referentialIntegrity.
For relational databases, the available options are:
foreignKeys: this handles relations in the database with foreign keys. This is the default option for all relational database connectors and is active if norelationModeis explicitly set in thedatasourceblock.prisma: this emulates relations in Prisma Client. You should also enable this option when you use the MySQL connector with a PlanetScale database.
For MongoDB, the only available option is the prisma relation mode. This mode is also active if no relationMode is explicitly set in the datasource block.
If you switch between relation modes, Prisma will add or remove foreign keys to your database next time you apply changes to your schema with Prisma Migrate or db push. See Switch between relation modes for more information.
Handle relations in your relational database with the foreignKeys relation mode
The foreignKeys relation mode handles relations in your relational database with foreign keys. This is the default option when you use a relational database connector (PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite, SQL Server, CockroachDB).
The foreignKeys relation mode is not available when you use the MongoDB connector. Some relational databases, such as PlanetScale, also forbid the use of foreign keys. In these cases, you should instead emulate relations in Prisma with the prisma relation mode.
Referential integrity
The foreignKeys relation mode maintains referential integrity at the database level with foreign key constraints and referential actions.
Foreign key constraints
When you create or update a record with a relation to another record, the related record needs to exist. Foreign key constraints enforce this behavior in the database. If the record does not exist, the database will return an error message.
Referential actions
When you update or delete a record with a relation to another record, referential actions are triggered in the database. To maintain referential integrity in related records, referential actions prevent changes that would break referential integrity, cascade changes through to related records, or set the value of fields that reference the updated or deleted records to a null or default value.
For more information, see the referential actions page.
Introspection
When you introspect a relational database with the db pull command with the foreignKeys relation mode enabled, a @relation attribute will be added to your Prisma schema for relations where foreign keys exist.
Prisma Migrate and db push
When you apply changes to your Prisma schema with Prisma Migrate or db push with the foreignKeys relation mode enabled, foreign keys will be created in your database for all @relation attributes in your schema.
Emulate relations in Prisma with the prisma relation mode
The prisma relation mode emulates some foreign key constraints and referential actions for each Prisma Client query to maintain referential integrity, using some additional database queries and logic.
The prisma relation mode is the default option for the MongoDB connector. It should also be set if you use a relational database that does not support foreign keys. For example, if you use PlanetScale you should use the prisma relation mode.
There are performance implications to emulation of referential integrity in Prisma Client, because it uses additional database queries to maintain referential integrity. In cases where the underlying database can handle referential integrity with foreign keys, it is usually the preferred choice.
Emulation of relations is only available for Prisma Client queries and does not apply to raw queries.
Which foreign key constraints are emulated?
When you update a record, Prisma will emulate foreign key constraints. This means that when you update a record with a relation to another record, the related record needs to exist. If the record does not exist, Prisma Client will return an error message.
However, when you create a record, Prisma does not emulate any foreign key constraints. You will be able to create invalid data.
Which referential actions are emulated?
When you update or delete a record with related records, Prisma will emulate referential actions.
The following table shows which emulated referential actions are available for each database connector:
| Database | Cascade | Restrict | NoAction | SetNull | SetDefault |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PostgreSQL | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌‡ | ✔️ | ❌† |
| MySQL | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌† |
| SQLite | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌‡ | ✔️ | ❌† |
| SQL Server | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌† |
| CockroachDB | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌��† |
| MongoDB | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌† |
- † The
SetDefaultreferential action is not supported in theprismarelation mode. - ‡ The
NoActionreferential action is not supported in theprismarelation mode for PostgreSQL and SQLite. Instead, use theRestrictaction.
Error messages
Error messages returned by emulated constraints and referential actions in the prisma relation mode are generated by Prisma Client and differ slightly from the error messages in the foreignKeys relation mode:
Example:
// foreignKeys:
... Foreign key constraint failed on the field: `ProfileOneToOne_userId_fkey (index)`
// prisma:
... The change you are trying to make would violate the required relation 'ProfileOneToOneToUserOneToOne' between the `ProfileOneToOne` and `UserOneToOne` models.
Introspection
When you introspect a database with the db pull command with the prisma relation mode enabled, relations will not be automatically added to your schema. You will instead need to add any relations manually with the @relation attribute. This only needs to be done once – next time you introspect your database, Prisma will keep your added @relation attributes.
Prisma Migrate and db push
When you apply changes to your Prisma schema with Prisma Migrate or db push with the prisma relation mode enabled, Prisma will not use foreign keys in your database.
Indexes
In relational databases that use foreign key constraints, the database usually also implicitly creates an index for the foreign key columns. For example, MySQL will create an index on all foreign key columns. This is to allow foreign key checks to run fast and not require a table scan.
The prisma relation mode does not use foreign keys, so no indexes are created when you use Prisma Migrate or db push to apply changes to your database. You instead need to manually add an index on your relation scalar fields with the @@index attribute (or the @unique, @@unique or @@id attributes, if applicable).
Index validation
If you do not add the index manually, queries might require full table scans. This can be slow, and also expensive on database providers that bill per accessed row. To help avoid this, Prisma warns you when your schema contains fields that are used in a @relation that does not have an index defined. For example, take the following schema with a relation between the User and Post models:
datasource db {
provider = "mysql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
relationMode = "prisma"
}
model User {
id Int @id
posts Post[]
}
model Post {
id Int @id
userId Int
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
}
Prisma displays the following warning when you run prisma format or prisma validate:
With `relationMode = "prisma"`, no foreign keys are used, so relation fields will not benefit from the index usually created by the relational database under the hood. This can lead to poor performance when querying these fields. We recommend adding an index manually.
To fix this, add an index to your Post model:
model Post {
id Int @id
userId Int
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
@@index([userId])
}
If you use the Prisma VS Code extension (or our language server in another editor), the warning is augmented with a Quick Fix that adds the required index for you:
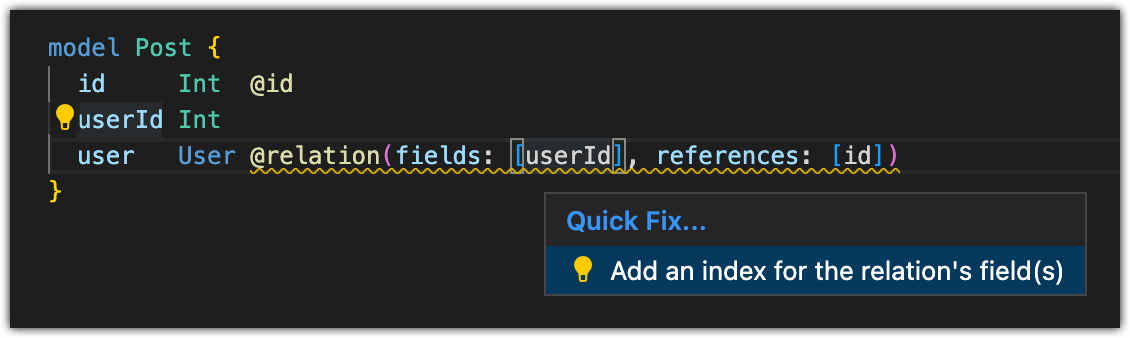
Switch between relation modes
It is only possible to switch between relation modes when you use a relational database connector (PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite, SQL Server, CockroachDB).
Switch from foreignKeys to prisma
The default relation mode if you use a relational database and do not include the relationMode field in your datasource block is foreignKeys. To switch to the prisma relation mode, add the relationMode field with a value of prisma, or update the relationMode field value to prisma if it already exists.
When you switch the relation mode from foreignKeys to prisma, after you first apply changes to your schema with Prisma Migrate or db push Prisma will remove all previously created foreign keys in the next migration.
If you keep the same database, you can then continue to work as normal. If you switch to a database that does not support foreign keys at all, your existing migration history contains SQL DDL that creates foreign keys, which might trigger errors if you ever have to rerun these migrations. In this case, we recommend that you delete the migrations directory. (If you use PlanetScale, which does not support foreign keys, we generally recommend that you use db push rather than Prisma Migrate.)
Switch from prisma to foreignKeys
To switch from the prisma relation mode to the foreignKeys relation mode, update the relationMode field value from prisma to foreignKeys. To do this, the database must support foreign keys. When you apply changes to your schema with Prisma Migrate or db push for the first time after you switch relation modes, Prisma will create foreign keys for all relations in the next migration.